
Lavender Stem; Typical Dicot Stem; Cross Section
The simulation "Stem Anatomy of Monocots and Dicots" aims to investigate the stem anatomy of monocot and dicot plants. The study of the internal structure of plants is called anatomy. Different organs in a plant show differences in their internal structure. Within angiosperms, the monocots and dicots are also seen to be anatomically.
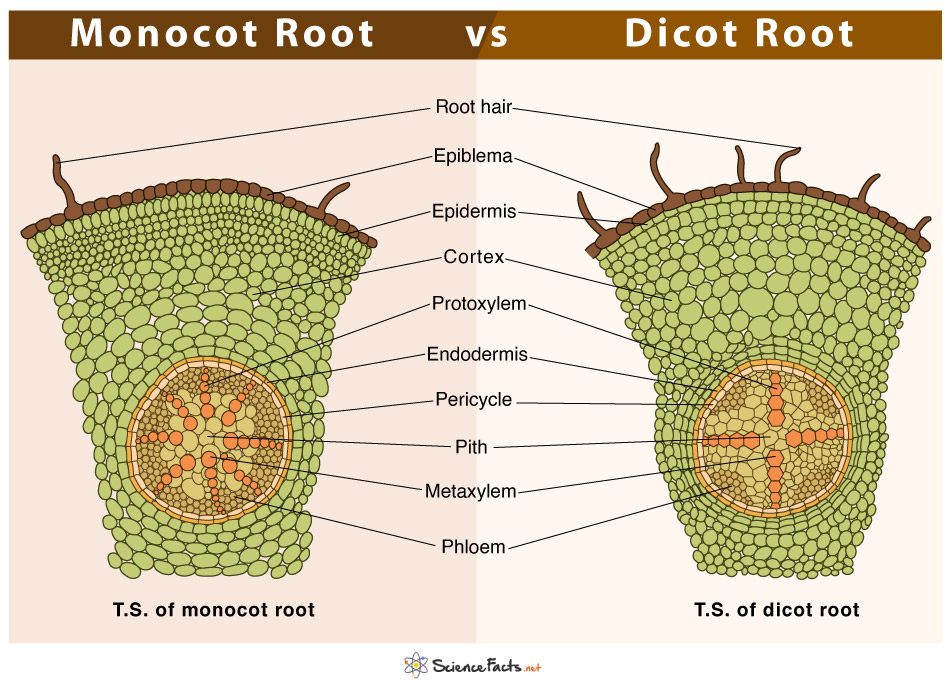
Monocot vs. Dicot Root Differences and Similarities
The dicotyledons, also known as dicots (or, more rarely, dicotyls ), [2] are one of the two groups into which all the flowering plants (angiosperms) were formerly divided. The name refers to one of the typical characteristics of the group: namely, that the seed has two embryonic leaves or cotyledons.

What are secondary growth in dicot stem? Definition, Types and Importance biology AESL
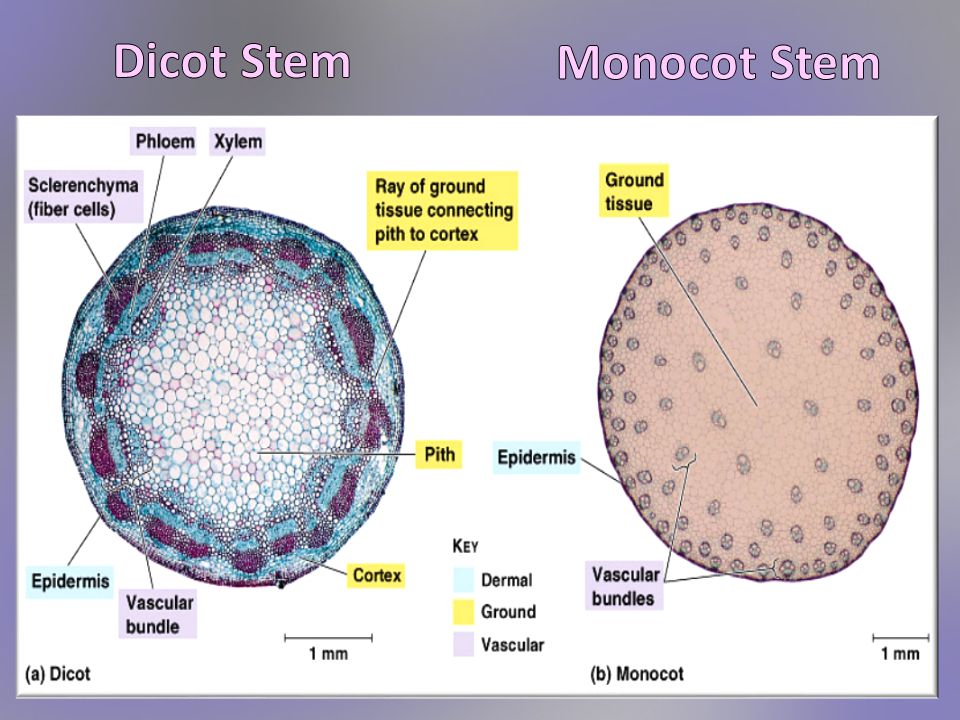
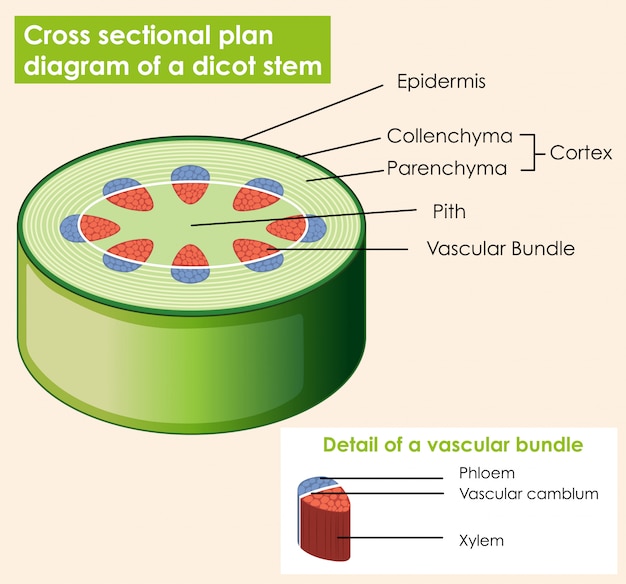
In monocot stems, the vascular bundles are randomly scattered throughout the ground tissue. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Vascular bundles: In (a) dicot stems, vascular bundles are arranged around the periphery of the ground tissue. The xylem tissue is located toward the interior of the vascular bundle; phloem is located toward the exterior.
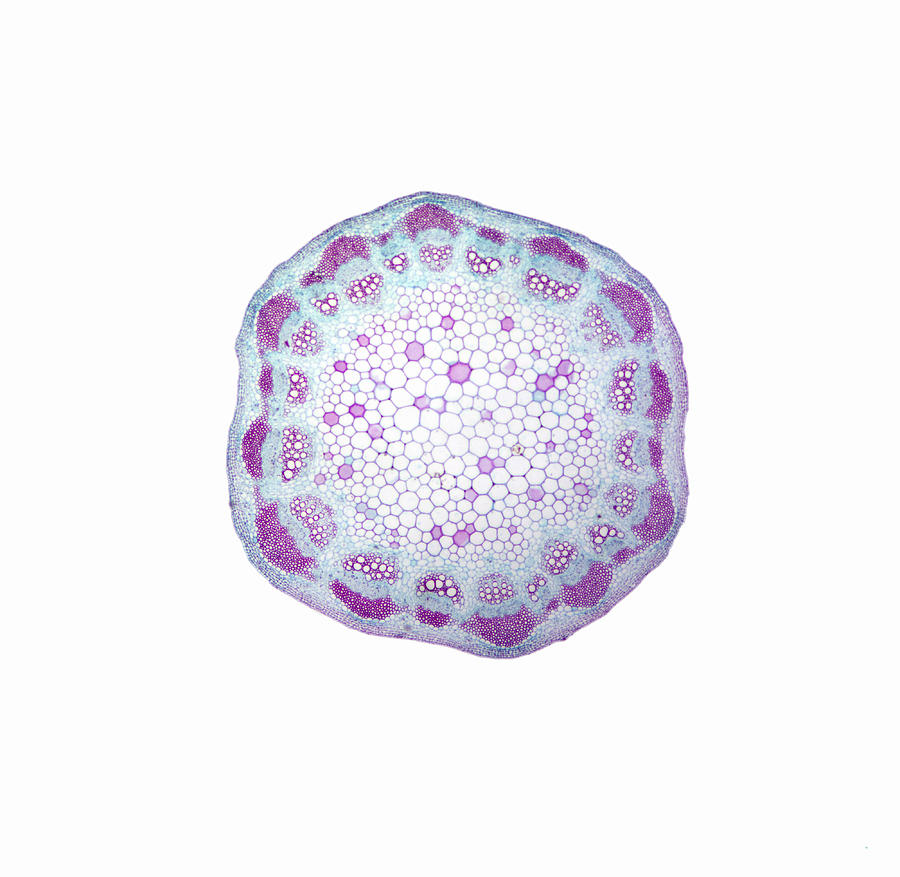
Dicot Stem Cross Section Herbaceous Stem Cross Sections Carlson Stock Art / In dicot plants
Dicotyledon, or dicot for short, refers to one of two main groups into which flowering plants (angiosperms) are categorized. Most flowering plants are traditionally divided into two different categories: monocots and dicots. Members of each group tend to share similar features.
Differences between Dicot and Monocot stem Online Science Notes
Monocot stems are a circular-shaped stem with lateral branches and are bounded with a layer of the dermis. Dicot stems have a well-defined epidermis with cuticle, a layer of dermis along with multicellular stem hair. Epidermal hair. In this multicellular epidermal hair are present over the epidermis. In this the epidermal hair is absent.
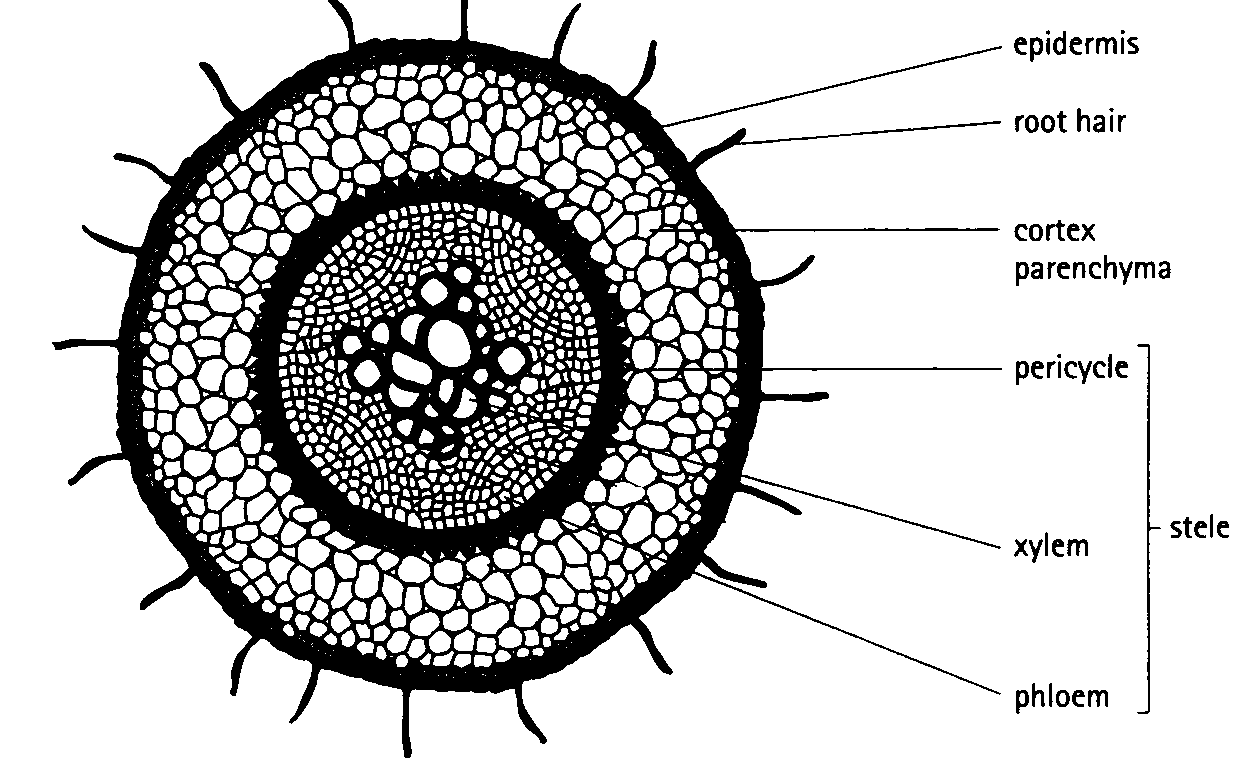
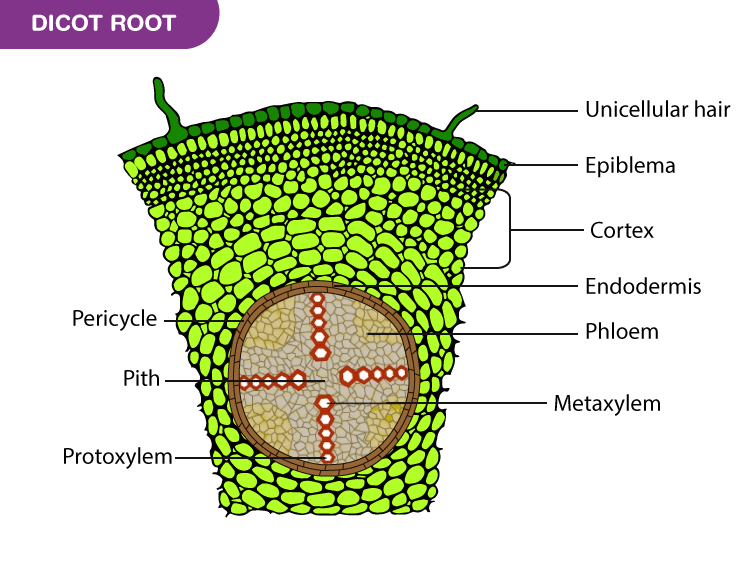
Internal structure of the dicot root By OpenStax Jobilize
April 11, 2019. by Lakna. 6 min read. The main difference between monocot stem and dicot stem is that monocot stem contains scattered vascular bundles across the stem whereas dicot stem contains vascular bundles arranged in the form of one or two rings . Monocot stem and dicot stem are the two types of stem structures in flowering plants.
5.2 Inside Stems The Science of Plants
ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the two typical dicotyledonous plants which been selected for the study of internal structure of stem with the help of diagrams. 1. Young Sunflower Stems (Figs. 146 & 147): If a thin and uniform transverse section is taken from a young sunflower stem and observed under the […]

Primary Structure of Dicot Stem
Plants have cells as the fundamental unit, cells are coordinated into tissues and thus the tissues are coordinated into organs. Various organs in a plant show contrast in their inward construction. Inside angiosperms, the monocots and dicots are likewise seen to be physically unique. Inner designs additionally show transformations to different.
Preparation And Study Of T.S Of Dicot And Monocot Roots And Stems(Primary)
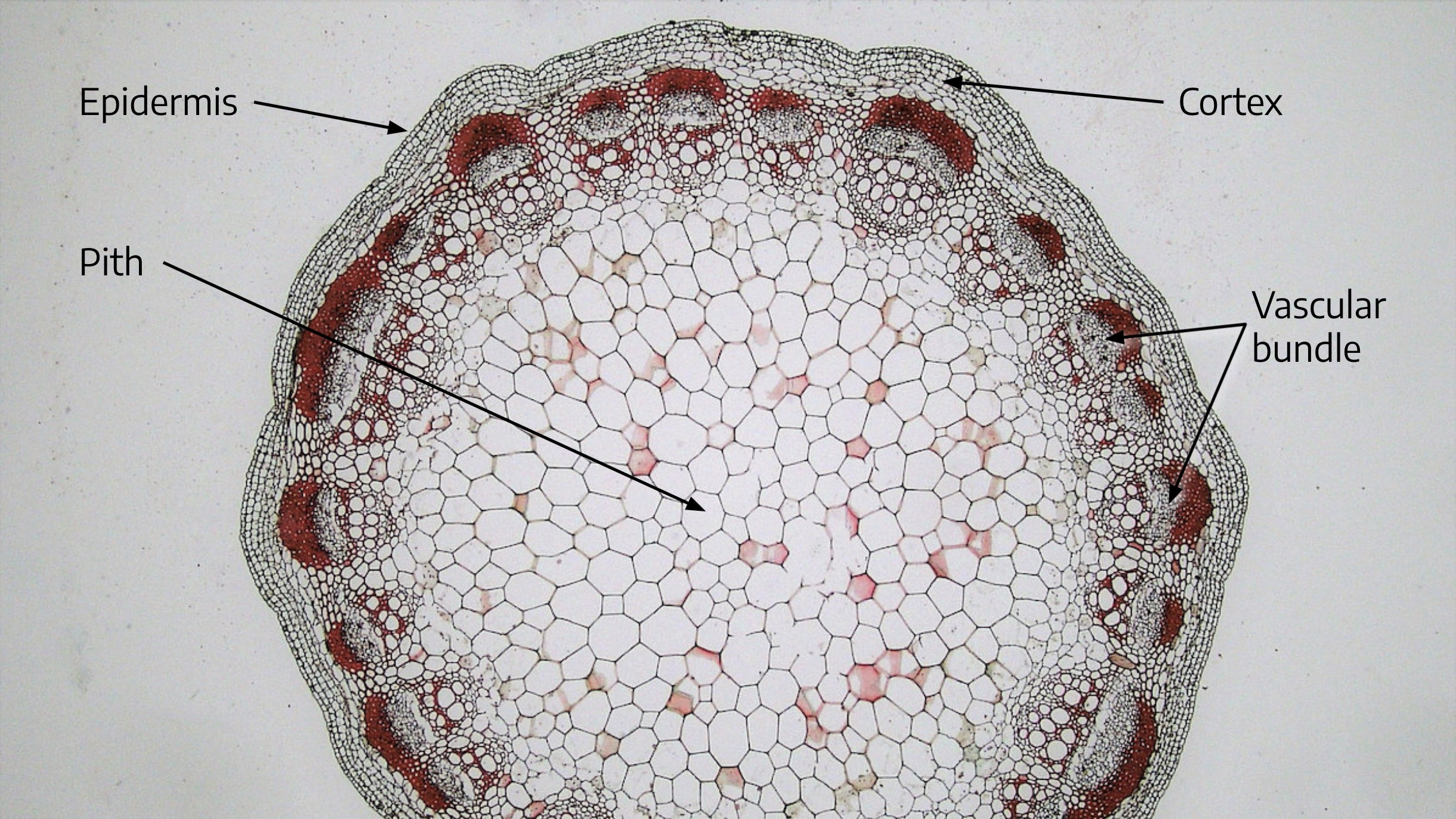
Anatomical structure of dicot stem T.S. of dicot stem shows following internal features: Epidermis: It is the outermost layer and has a single layer of parenchymatous cells. It possesses stomata and large number of multicellular hairs (trichomes). The outer walls are greatly thickened and cutinized.
Free Vector Diagram showing cross sectional plat of dicot stem
Examples of Dicot Stem Cactus stem References and Sources Definition of Monocot Stem Monocot stem is a circular-shaped hollow axial part of the plant which gives rise to nodes, internodes, leaves, branches, flowers with roots at the basal end. The size of stems varies in different species of monocots, but the size is barely ever as large as dicots.

What is Dicot Root? Definition, Structure, Characteristics, Examples
Dicotyledon plants, or simply dicots, are those whose seed include two cotyledons or embryonic leaves. This section will teach you about the properties and anatomy of the dicot stem. Dicot stems feature a circular arrangement of vascular tissues, whereas monocot stems contain vascular-tissue bundles distributed throughout. In monocots, the vascular bundles are also found on the outside of the.

Stem Cross Section Alfalfa Xylem Phloem Pith Cortex And Epidermis HighRes Stock Photo Getty
Epidermis is the outermost layer of (dicot) stem with multicellular epidermal stem hairs. The cells are living, barrel shaped and compactly arranged without intercellular spaces and chloroplasts. They may contain stomata for gaseous exchange. The epidermis is externally covered by thick cuticle.

Helianthus Herbaceous Dicot Stem Cross Section Vascular Bundles Cortex Pith 25x Foto de stock
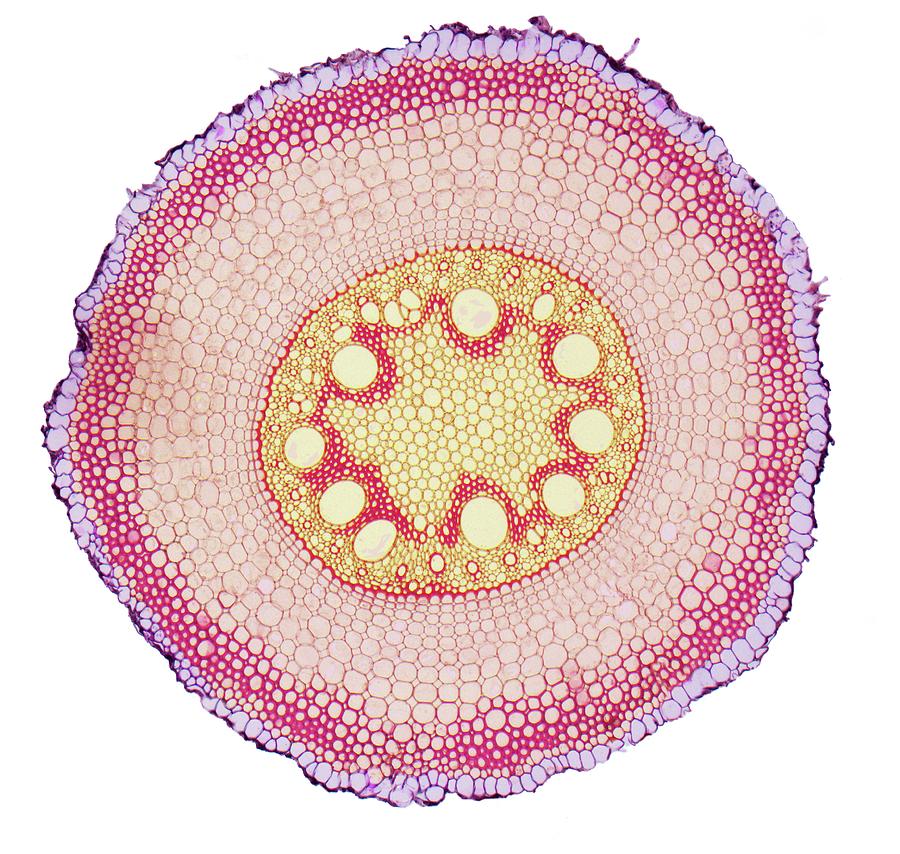
The dicot stems are stems of dicot plants. They are arranged concentrically, one above the other. The vascular bundles of dicot stems are arranged in a ring without a bundle sheath. However, parenchyma cells surround each vascular bundle in the dicot stem. The hypodermis of dicot stems is made of collenchymas cells.
.PNG)
Dicot Stem Cross Section Dicot Stem Anatomy Plant Science 4 U / The cuticle is transparent
Dicot stem In dicot stems, the vascular bundles are arranged in a ring. Like dicot roots, dicot stems are protected by an outer layer of dermal tissue called the epidermis. Then, also similar to dicot roots, dicot stems have a layer of ground tissue called the cortex beneath the epidermis.
Dicot Root Vascular Arrangement Photograph by Steve Gschmeissner/science Photo Library Pixels
The vascular bundles in the monocot stem are dispersed, whereas the monocot stem possesses vascular bundles in the ring pattern. The stem of monocots contains a closed-type of vascular system due to the absence of cambium. Oppositely, the stem of dicots comprises the open-type vascular system that includes cambium in between phloem and metaxylem.
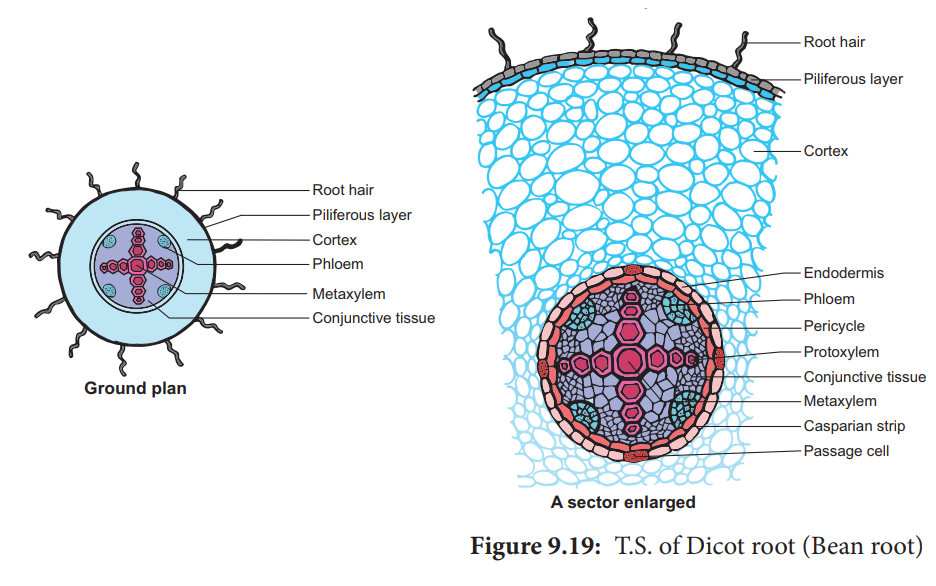
Internal structure of dicot root Online Biology Notes
When the stem is viewed in cross section, the vascular bundles of dicot stems are arranged in a ring. In plants with stems that live for more than one year, the individual bundles grow together and produce the characteristic growth rings. In monocot stems, the vascular bundles are randomly scattered throughout the ground tissue (Figure 30.9).